
主要研究方向和领域
面向新材料、能源与环境领域的关键问题与挑战,关注能量转换与存储过程,课题组围绕碳纳米材料、石墨烯、碳纳米管、导电与功能高分子的可控制备、功能修饰与组装等开展研究,探究其在先进功能材料、高效能量转化与储存等方面的应用。研究领域涉及纳米与材料化学、电化学、绿色能源、柔性电子与储能器件等,包括石墨烯超结构、智能响应高分子、海水淡化、空气发电、新型电化学电池/电容器、微型能源器件及柔性器件等。
|
|
|
先进功能材料 |
|
先进功能材料一直是国际科研的前沿和热点,是高科技发展的核心材料与基础。
重点围绕碳纳米材料、石墨烯、碳纳米管、导电高分子、纳米复合材料体系,通过本征结构调控,化学修饰/复合、纳米限域调控、微结构调控、宏观组装以及先进的微纳加工与制造技术等,深入研究其化学/物理性质,发展制备与加工新方法、新策略,获得具有新特性、新功能的先进功能材料。
|
 |
|
1. Graphene-Based Fibers: Recent Advances in Preparation and Application, Adv. Mater. 2019, 1901979. (Review)
2. Graphene-based smart materials, Nature Reviews Materials, 2017, 2, 17046. (Review)
3. Graphene-Based Functional Architectures: Sheets Regulation and Macrostructure Construction toward Actuators and Power Generators, Accounts of Chemical Research, 2017, 50 (7), 1663-1671. (Review)
4. Graphene platforms for smart energy generation and storage, Joule, 2018, 2, 245–268. (Review)
5. A General and Extremely Simple Remote Approach toward Graphene Bulks with In Situ Multifunctionalization, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(17), 3305-3312.
6. Metal-Free Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115(11), 4823–4892. (Review)
7. Tailored Graphene Systems for Unconventional Applications in Energy Conversion and Storage Devices, Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 8(1), 31–54. (Review)
8. Graphene Quantum Dots: An Emerging Material for the Energy-Related Applications and Beyond, Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5, 8869–8890. (Review)
9. Carbon nanotube arrays with strong shear binding-on and easy normal lifting-off, Science, 2008, 322, 238–242.
10. Shape/size-controlled syntheses of metal nanoparticles for site-selective modification of carbon nanotubes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128 (16): 5523–5532
|
|
| |
|
|
|
水发电技术 |
|
地球表面水覆盖约75%,水循环过程蕴含巨大能量。课题组在国际上首先提出了空气中水汽发电的新概念(Moisture enabled electricity generation, or Most-electric generation, MEG)。
石墨烯、高分子等通过有效的表面官能团调控,能够自发吸收空气中气态水分直接产生电能,也称“空气发电”。通过分子设计、化学改性、表面修饰、微纳加工等策略,开发了一系列高性能水汽发电新材料。借助激光加工、丝网印刷与3D打印技术实现高效水汽发电器件的制备与大规模集成,在大气环境中能够产生几百毫伏到几十伏的电压。进一步探索湿气发电技术在传感器、物联网、柔性电子、非接触式人机交互等领域的应用。同时,也发展了一系列液态水高效发电材料和器件(Water-enabled electricity generation, WEG)。
|
 |
|
1. All-region-applicable, continuous power supply of graphene oxide composite, Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12 (16), 1848–1856.
2. Rollable stretchable and reconfigurable graphene hygroelectric generators, Advanced Materials, 2019, 31 (2), 5705.
3. An efficient polymer Moist-Electric Generator. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12 (3), 972–978.
4. Interface-mediated hygroelectric generator with an output voltage approaching 1.5 volts. Nature Communications, 2018, 9, 4166.
5. Electric power generation through the direct interaction of pristine graphene-oxide with water molecules, Small, 2018, 1704473.
6. Graphene oxide nanoribbon assembly toward moisture-powered information storage, Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(3),1604972.
7. Highly efficient moisture-enabled electricity generation from graphene oxide frameworks, Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(3), 912–916.
8. Direct power generation of a graphene oxide film under moisture, Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(29), 4351–4357.
9. Emerging materials for Water-Enabled Electricity Generation, ACS Materials Letters, 2021, 3, 193–209. (Review)
10. Moist-electric generation, Nanoscale, 2019, 11 (48), 23083–23091. (Review)
|
|
| |
|
|
|
增强界面蒸发 |
|
常规蒸发、蒸馏过程比较低效,界面增强蒸发、蒸馏将革新传统液-汽转化过程,突破传统热蒸馏、海水淡化方式。课题组创新材料设计与制备,诱导水分子在微观界面的重新分布,开发了系列高效界面水蒸发材料,增强界面热利用和管理,有效降低能耗,大幅提升蒸发效率,实现了高效海水淡化、盐碱水纯化、污水净化、甚至空气中水汽的收集。同时,也设计了全新的界面蒸发蒸馏装置,实现了超节能的光热/电热水清洁及海水淡化装备系统,为水资源短缺问题提供了独特解决方案。
|
 |
|
1. Highly efficient solar vapour generation via hierarchically nanostructured gels, Nature Nanotechnology, 2018, 13, 489–495.
2. Highly efficient clean water production from contaminated air with a wide humidity range, Advanced Materials, 2020, 32 (6), 1905875.
3. Reduced graphene oxide-based spectrally selective absorber with an extremely low thermal emittance and high solar absorptance, Advanced Science, 2020, 1903125
4. Interface-enhanced distillation beyond tradition based on well-arranged graphene membrane. Sci. China-Mater. 2020, 63 (10), 1948–1956.
5. Plant leaves inspired sunlight-driven purifier for high-efficiency clean water production, Nature Communications, 2019, 10, 1512.
6. Direct solar steam generation system for clean water production, Energy Storage Materials, 2019, 18, 429–446. (Review)
7. Thermal Efficiency of Solar Steam Generation Approaching 100 % through Capillary Water Transport, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019,58(52): 19041–19046
8. High rate production of clean water based on the combined photo-electro-thermal effect of graphene architecture, Advanced Materials, 2018, 1706805.
9. Vertically Aligned Graphene Sheets Membrane for Highly Efficient Solar Thermal Generation of Clean Water", ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 5087–5093.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
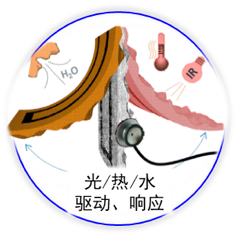
智能/仿生材料与结构 |
|
智能/仿生材料具有类生物体的功能或者特性(如亲/疏水性、类贝壳结构等),或者能够感知外界刺激(光、电、热、磁、水、酸、碱刺激等)并进行积极响应(膨胀/收缩、颜色变化、机械运动等)。
课题组通过合理设计、化学组成和物理微结构调控,发展了系列具有水汽诱导形变、光/电/磁刺激响应的碳基、高分子基功能材料与结构,并构建了水汽驱动的仿生爬行器、纤维“马达”、自感知“机器人”、智能微管道等。同时,发展了多种超亲水性,和超疏水性石墨烯功能材料等。
|
 |
|
1. A microstructured graphene/poly(n-isopropylacrylamide) membrane for intelligent solar water evaporation, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57 (50), 16343–16347.
2. Sunlight-driven water transport via a reconfigurable pump", Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57 (47), 15435–15440.
3. Self-healing graphene oxide based functional architectures triggered by moisture, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27 (42), 1703096
4. A responsive battery with controlled energy release, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 128(47), 14863–14867.
5. A graphene fibriform responsor for sensing heat, humidity, and mechanical changes, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(49), 14951–14955.
6. Moisture-activated torsional motor of graphene fiber, Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 2909–2913.
7. Environmentally responsive graphene systems, Small, 2014, 10(11), 2151–2164.
8. Stimulus-responsive graphene systemstowards actuator applications, Energy Environ. Sci., 2013, 6, 3520–3536. (Review)
9. Graphene fibers with predetermined deformation as moisture-triggered actuators and robots, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(40), 10482–10486.
10. Carbon nanotube arrays with strong shear binding-on and easy normal lifting-off, Science, 2008, 322, 238–242
|
|
| |
|
|
|
高性能能源器件 |
|
面向电化学储能器件,研制高性能电极材料,实现高能量密度、高功率密度、高质量/体积容量的新型电池、超级电容器;
面向柔性、可穿戴、微型化储能需求,发展了印刷、激光加工、3D打印等方法技术实现大面积电容、电池器件的柔性集成。
面向电化学产氢、产氧,光催化水分解,工业催化等领域,构建了纳米量子点、纳米线、纳米网等系列高性能催化材料。
|
 |
|
1. Compact assembly and programmable integration of supercapacitors, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907005.
2. Arbitrary waveform AC line filtering applicable to hundreds of volts based on aqueous electrochemical capacitors, Nature Commun. 2019, 10: 2855
3. Efficient metal-free electrocatalysts from n-doped carbon nanomaterials: mono-doping and co-doping”, Adv. Mater. 2018, 1805121.
4. Integrated graphene systems by laser irradiation for advanced devices”, Nano Today, 2017, 12, 14–30.
5. A Graphitic-C3N4 "Seaweed" architecture for enhanced hydrogen evolution”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(39), 11433–11437.
6. Metal-free catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction”, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115(11), 4823–4892.
7. All-graphene core-sheath microfibers for all-solid-state, stretchable fibriform supercapacitors and wearable electronic textiles”, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25(16), 2326–2331.
8. Highly compression-tolerant supercapacitor based on polypyrrole-mediated graphene foam electrodes”, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25(4), 591–595
9. Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots with oxygen-rich functional groups”, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012 134 (1), 15–18.
10. An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron-acceptors for photovoltaics, Adv. Mater., 2011, 23, 776–780.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
特种功能材料 |
|
通过纳米微结构调控、化学组成改性等方法,并结合生长与组装策略,发展了系列特殊性能材料,涉及石墨烯纤维,高导热石墨烯薄膜,超弹、超轻石墨烯泡沫等,相关特种石墨烯功能材料在航天航空、超灵敏感应、高效电磁屏蔽、吸波隔音、耐火耐热、抗腐蚀等方面具有特殊的应用价值。
|
 |
|
1. Graphene-based fibers: recent advances in preparation and application, Adv. Mater. 2019, 1901979.
2. Reconstruction of inherent graphene oxide liquid crystals for large-scale fabrication of structure-intact graphene aerogel bulk toward practical applications, ACS Nano, 2018,12(11), 11407-11416.
3. A general and extremely simple remote approach toward graphene bulks with in situ multifunctionalization, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(17), 3305-3312.
4. Scalable preparation of multifunctional fire-retardant ultralight graphene foams, ACS Nano, 2016, 10 (1), 1325-1332.
5. A large-area, flexible, and flame retardant graphene paper, Adv. Func. Mater., 2016, 26(9), 1470-1476.
6. A powerful approach to functional graphene hybrids for high performance energy-related applications, Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7 (11), 3699–3708.
7. Functional graphene nanomesh foam, Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7, 1913–1918.
8. Graphene microtubings: controlled fabrication and site-specific functionalization, Nano Lett., 2012, 12 (11), 5879–5884.
9. A versatile, ultralight, nitrogen-doped graphene framework, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 124(45), 11533–11537.
10. Facile fabrication of light, flexible and multifunctional graphene fibers, Adv. Mater., 2012, 24 (14), 1856–1861.
|
|
| |
|
|
|